Mechatronics Engineering
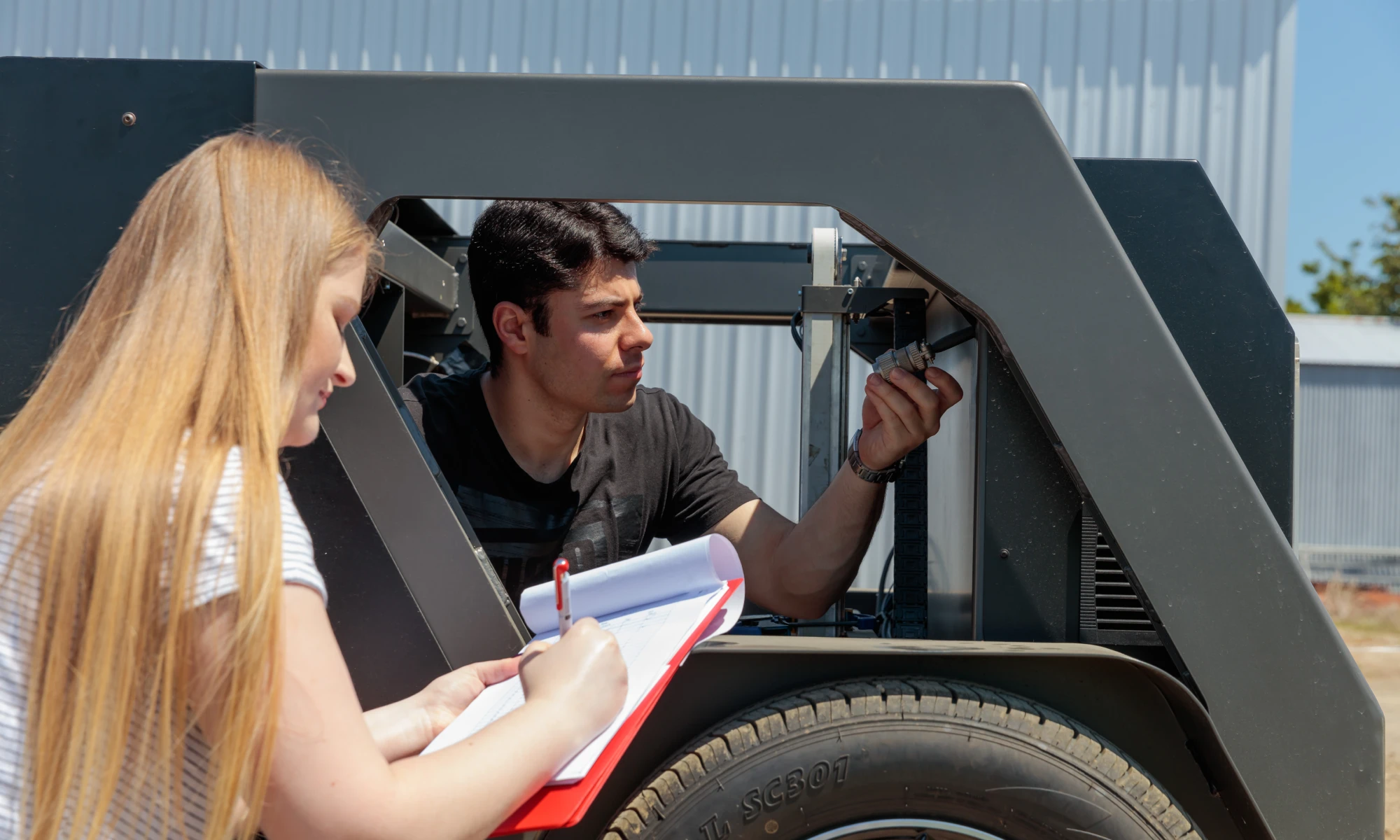

Why study Mechatronics Engineering?
Mechatronics engineers are trained to be masters of intelligent machines and work across many industries, making the latest “Smart Systems” work for us.
The Mechatronics programme from the University of Waikato School of Engineering has a strong focus on integrating agriculture and infrastructure with software-hardware interfacing technology. The emphasis is on design-and-build projects and on a truly interdisciplinary approach combining computer science, electrical & electronic engineering and mechanical engineering that will equip you for jobs of the future.
The demand of workers well-versed with intelligent and networked robotics, electronics and mechanical engineering systems is increasing both nationally and internationally. Mechatronics engineers are skilled in creating innovative solutions to overcome the challenges of the information-age society. The close working relationship between the School of Engineering and industry partners means you will have a broad range of options available for required work placements and applied research projects.
You'll work on major research design projects, creating products with commercial applications, which are then showcased at our annual Engineering Design Show. Importantly, there is also a focus on developing well-honed transferable skills that are such a vital part of the profession.
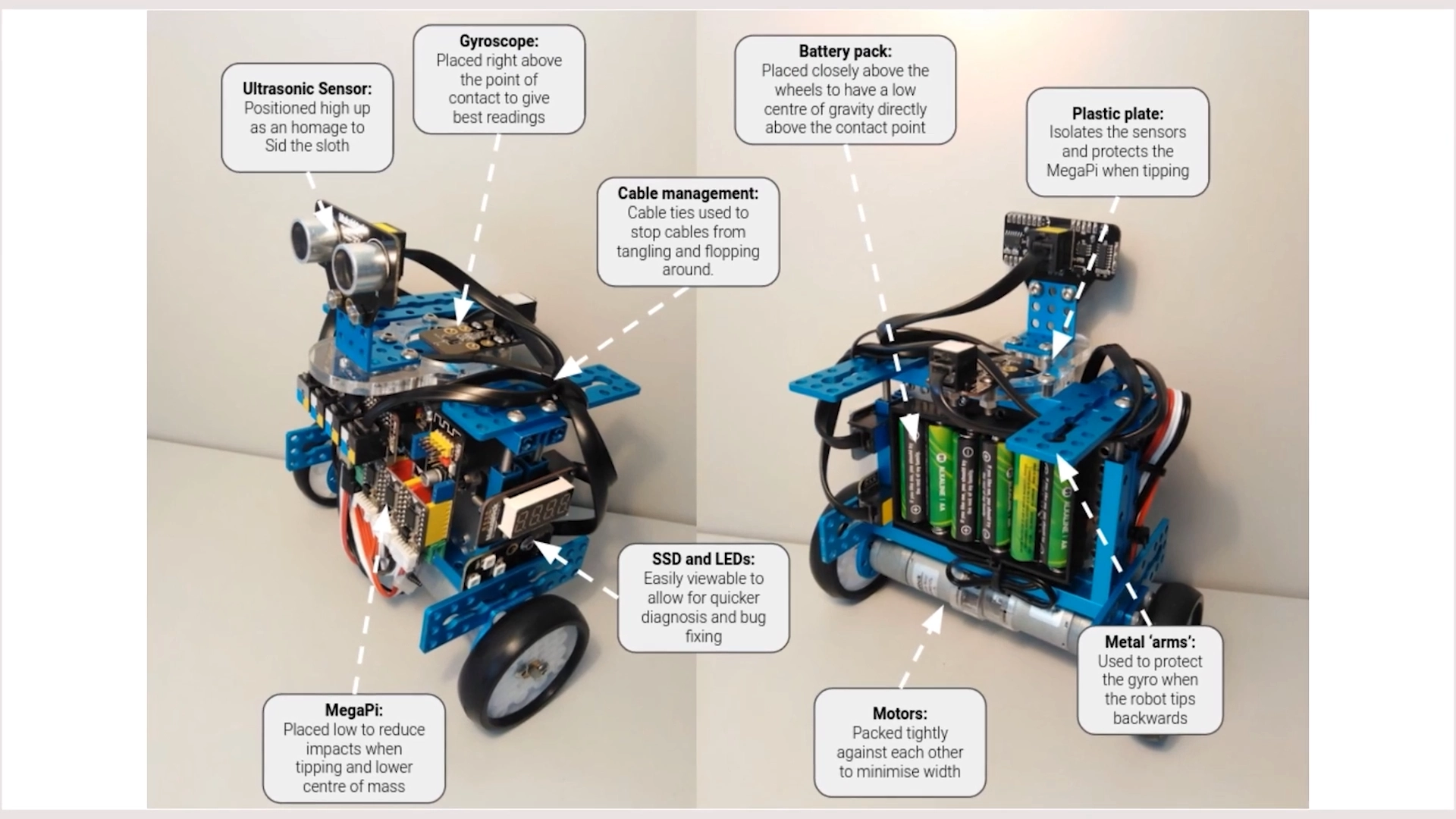
Career opportunities
- Mechatronics engineer
- Robotics Engineer
- Automation Engineer
- Control Engineer
- Systems Engineer
- Instrumentation Engineer
- Computer-aided Engineer
- Product Design and Development
- Project Manager
Study Mechatronics Engineering in these qualifications
Accreditation
The Mechatronics Engineering programme has provisional accreditation under the Washington Accord and will be eligible for full accreditation in 2025.
Practical engineering experience
Work placements are a major feature of the Mechatronics Engineering programme and you will complete 800 hours of relevant work experience during your engineering degree.
Our Work-Integrated Learning team actively seeks and oversees your work placement, ensuring a good fit for your area of study and career goals, and supporting you throughout your work experience.
By the time you graduate you will have the credibility of paid experience to take with you as you start your career.
Facilities
Students can work in specialised laboratories including the Large Scale Lab (Mata - Tina) complex that features a suite of workshops and laboratories dedicated to engineering, teaching and research, such as 3D printing, a mechanical workshop and computer labs with engineering design software. Students who demonstrated outstanding performance and dedication will be offered opportunities to take part in the development of the latest technology host by WaiRAS research group.
Build a successful career
Industry 4.0 will create a stable global demand for Mechatronics Engineering graduates. As a Mechatronics Engineering graduate you could work in a range of exciting fields that covers mechanical, electrical, electronics or software design and development. You may be building and operating intelligent robots, implementing the latest artificial intelligent algorithm for automation, be a specialist in instrumentation and control engineering, overseeing large engineering projects as system engineer; or use your inter-personal, numeracy and data processing skills to become an effective professional manager.
New Zealand, in particular, will benefit from the application of the “smart” technology in high-value food production (dairy, meat and horticulture), forestry, various high-value manufacturing, infrastructure upgrade and large-scale environment surveillance.
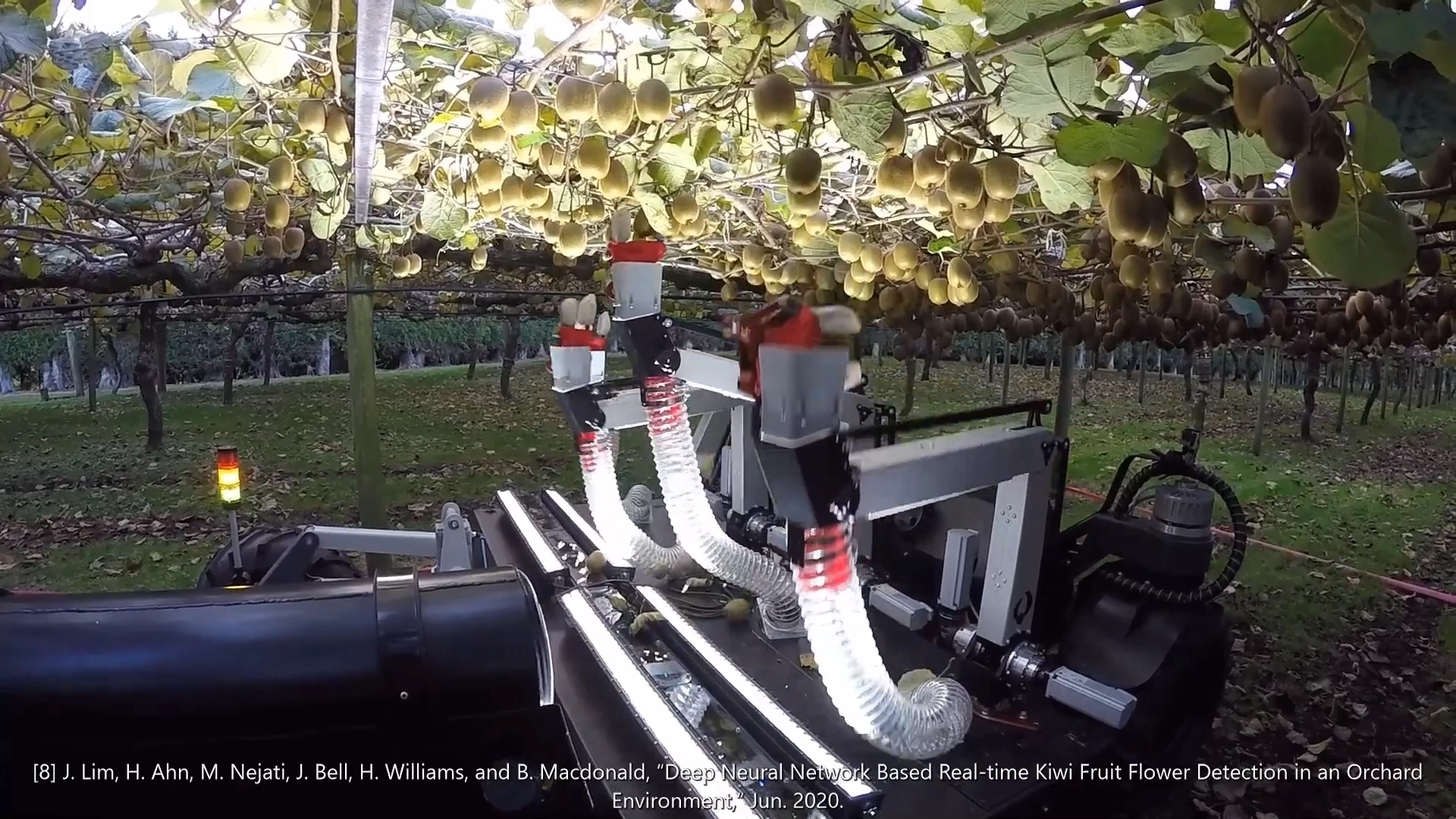

Replication of orchard/farm dynamic environments with a physical platform
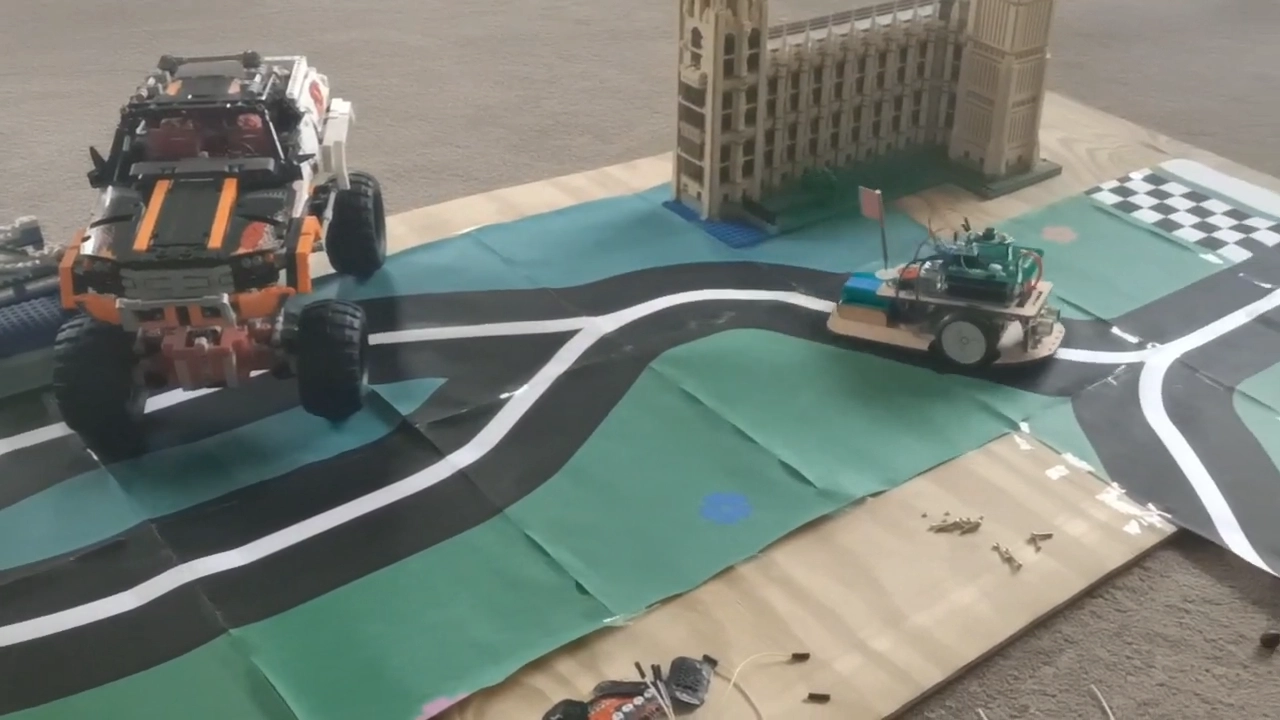
Smart Autonomous Vehicles - Grand Challenge!
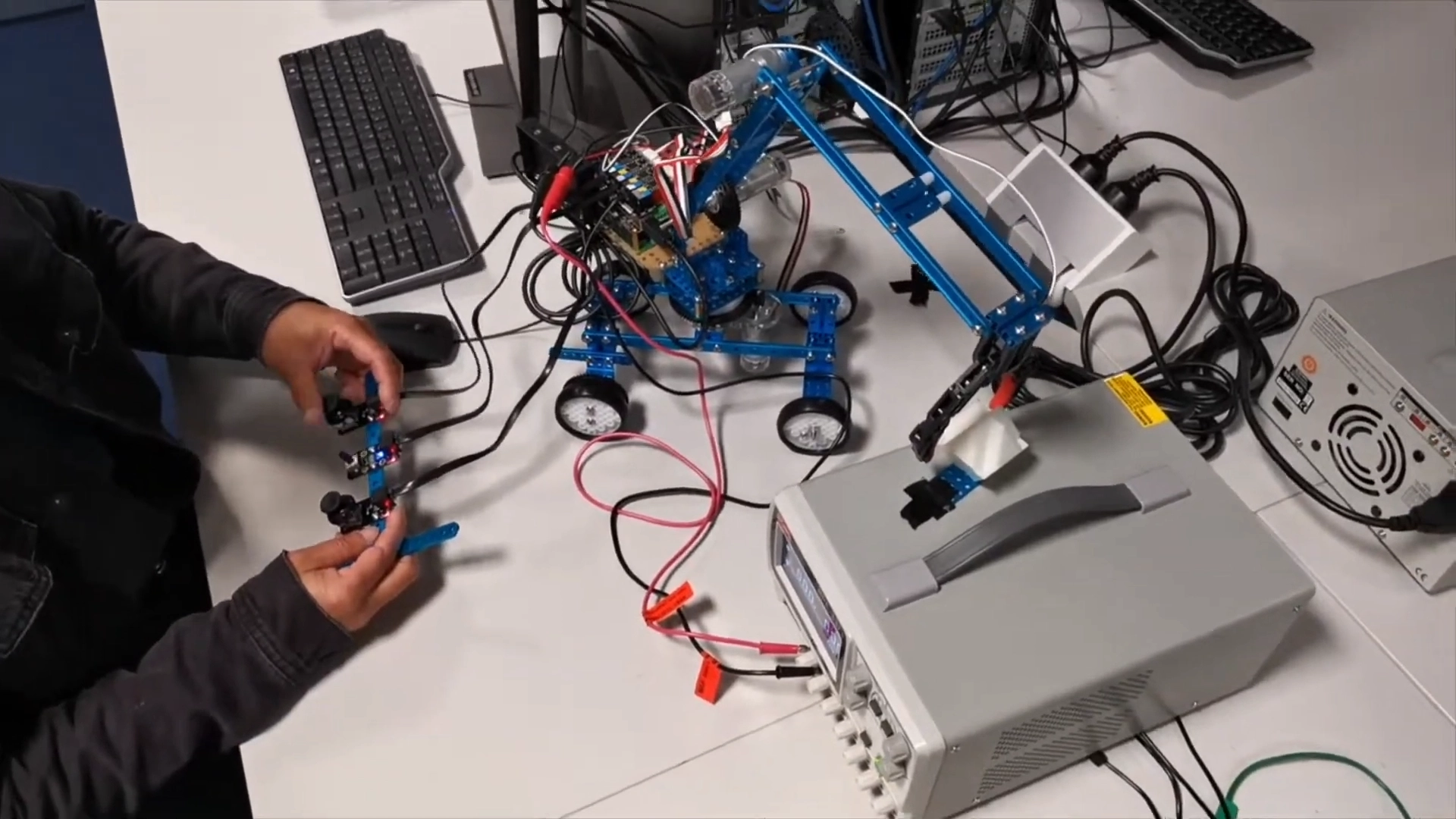
Crane Robot Teaching
Scholarships and prizes
Visit our Scholarship Finder for information about possible scholarships